2005 Answers
These are my answers and explanations for them. If you really disagree with me, or are unsure of my explanation, feel free to yell at me. Yes, I actually looked at the book, notes, and the internet to do this.
1. D
In the book, there were two types of economies listed. In one economy, it was completely determined by market. In the more controlling economy, things were controlled by the government. There's no such thing as a planning agency, so D looks good to me. Markets can decide what they want, and the government can pay people to make things too.
2. C
Real is always adjusted for inflation, nominal is always just an increase.
3. E
Structural employment is the one where you have a mismatch of skills and are in the wrong location.
4. D
So everyone's freaking out because their apples are now poisonous. So instead, they all go out and buy pears. It is not C or E, because the demand for pears will not go down. THE SUPPLY DOES NOT CHANGE. The farmers didn't decide to grow more pears all of a sudden, there are a set amount of pears, and that's it. D because demand does go up for pears, while the supply stays the same.
5. C
All the other answers are bullshit, so this one is pretty much common sense.
6. B
If people have large unpaid balances on their credit cards, they would stop spending. If the government encourages people to save, they might actually listen. Nobody gives a shit about social security taxes except old people, and if people don't think they'll make a lot of money next year, they won't spend it all now. If people got more wealth from the stock market, they would feel like rich fat cats and spend more, so the answer is B.
7. B
This was straight from the book, the crowding out effect is when private consumption and investment is decreased because of increased government spending. Hence, canceling or crowding each other out.
8. A
Fractional reserve is when banks have to keep a certain percentage of their deposits as a reserve. C is not right, banks don't insure money, the FDIC insures money.
9. B
An increase in taxes lowers aggregate demand because people have less to spend. Increasing the federal funds, the reserve requirement, or the discount rate only makes it harder for banks to loan out money. An increase in government spending will increase the money supply, giving more money for people to spend, which increases aggregate demand.
10. C
The government doesn't get more money to spend by increasing the reserve ratio. There's no such thing as the World Bank, so B is wrong. D and E are wrong, the government can't just magically decide to make the dollar worth more or less. If they issue new bonds, they get more money from people to spend, so the answer is C.
11. A
Taxes aren't affected by the Federal Reserve buying bonds from people. The money supply will increase because the Federal Reserve just gave people money for their bonds. If people have more money, investment will increase, not decrease. When the Feds buy bonds, they also decrease the discount rate. By decreasing the discount rate, banks can now afford to offer a lower interest rate, which will result in more people loaning money.
12. E
Quantity and quality of humans and resources will affect the supply of products, so that will affect the growth of the economy. If there are more capital goods available, then businesses can have more machines and make more goods. Also, better technology would affect the growth of the economy too.
13. D
The Phillips curve is a relation and trade off between the rate of unemployment and the rate of inflation.
14. B
Okay, assume gasoline just got cheaper. That means it will now cost businesses less to make goods, so now they lower their prices. That eliminates C, D, and E.
 Price level goes down, and output increases.
15. D
A is wrong. There's no such thing as world inflation. If workers suffer, businesses will always end up suffering. For E, notice the words "free international trade" which means that we wouldn't tax anything. We do tax things from other countries, and that reason is so people are encouraged buy American goods, since foreign goods won't be the cheapest anymore aka protecting United States industries.
16. D
85 - 70 = 15
17. C
It's right in the middle, and it looks like it would be the best combination for producing the maximum amount of belts and coats together.
18. A
The labor force is the amount of people who are either looking or have a job. The unemployment rate measures the percentage of people who are are either looking or have a job. Therefore, the unemployment rate measures the amount of people in the labor force who do not have jobs.
19. C
This was in the book. The classical economists all believed in laissez faire, which means the market would be self-correcting and manage itself.
20. E
C+I+G+X. What's missing?
21. B
An increase in MPC means that people are spending more. That eliminates A and C. The more people spend per consumer, the higher the multiplier. The multiplier is
Price level goes down, and output increases.
15. D
A is wrong. There's no such thing as world inflation. If workers suffer, businesses will always end up suffering. For E, notice the words "free international trade" which means that we wouldn't tax anything. We do tax things from other countries, and that reason is so people are encouraged buy American goods, since foreign goods won't be the cheapest anymore aka protecting United States industries.
16. D
85 - 70 = 15
17. C
It's right in the middle, and it looks like it would be the best combination for producing the maximum amount of belts and coats together.
18. A
The labor force is the amount of people who are either looking or have a job. The unemployment rate measures the percentage of people who are are either looking or have a job. Therefore, the unemployment rate measures the amount of people in the labor force who do not have jobs.
19. C
This was in the book. The classical economists all believed in laissez faire, which means the market would be self-correcting and manage itself.
20. E
C+I+G+X. What's missing?
21. B
An increase in MPC means that people are spending more. That eliminates A and C. The more people spend per consumer, the higher the multiplier. The multiplier is
 So let's say that the MPC is .3
So let's say that the MPC is .3
 The multiplier is 1.42. Now let's increase the MPC to .6
The multiplier is 1.42. Now let's increase the MPC to .6
 Since the MPC increased, the multiplier has increased too.
22. B
Mexicans just gave us all their worthless Pesos, so the supply of those increased. Since we got a whole bunch of them now, their value goes down.
23. D or A
Well, the answer is not $1,000 so E is out. $10,000 is not right either, because they have to store $1000 in the reserves, they just can't lend out all of it. $90,333 looks stupid. If a customer deposits $10,000 it would make complete sense that the bank can loan out $9000 now. It's a tossup between whether you want to use some crazy multiplier or not, so the answer can be either $100,000 or $9,000 depending on how smart you are.
24. D
Increases in government spending will raise the income level of consumers. It will also raise the price level, as shown here.
Since the MPC increased, the multiplier has increased too.
22. B
Mexicans just gave us all their worthless Pesos, so the supply of those increased. Since we got a whole bunch of them now, their value goes down.
23. D or A
Well, the answer is not $1,000 so E is out. $10,000 is not right either, because they have to store $1000 in the reserves, they just can't lend out all of it. $90,333 looks stupid. If a customer deposits $10,000 it would make complete sense that the bank can loan out $9000 now. It's a tossup between whether you want to use some crazy multiplier or not, so the answer can be either $100,000 or $9,000 depending on how smart you are.
24. D
Increases in government spending will raise the income level of consumers. It will also raise the price level, as shown here.
 Increases in government spending will make the money supply larger and will not affect bond prices. This will cause inflation. To combat inflation, interest rates will be increased.
25. D
Long-run economic growth always has a vertical aggregate supply curve, so that eliminates A, B, and E. Growth of the economy will happen when the money supply increases, as demonstrated in graph D.
26. A
Stagflation is when the price level is increasing while the unemployment rate increases and slow output growth. Moving the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left will demonstrate this by increasing the price level and lowering output.
27. B
The money supply of Country X will go down because of higher interest rates. This will make their currency worth more, and since it has increased in value, Country Y can't afford as many exports from that country, so exports will decrease.
28. D
When they sell bonds on the market, they will decrease the money supply, since people are giving them money for bonds. When they sell bonds, they also increase the discount rate, which will cause an increase in interest rates.
29. B
C, D, and E are just stupid. I never even heard of A happening.
30. E
The long-run Phillips curve is a vertical line that represents the natural rate of unemployment. A and B only apply to the short-run curve. The idea is that even if the natural rate of unemployment changes, it will always revert back to normal in time, meaning it will not be affected by monetary and fiscal policy changes that affect aggregate demand. Really, I'm not making this stuff up.
31. C
Page 200 in the book has changes of input prices, changes in productivity, and changes in government regulations listed as determinants. Government spending is a determinant of aggregate demand, NOT aggregate supply. The price level is changed based the direction that the aggregate supply curve shifts, so the only possible choice is cost of input prices.
32. B
Increases in government spending will make the money supply larger and will not affect bond prices. This will cause inflation. To combat inflation, interest rates will be increased.
25. D
Long-run economic growth always has a vertical aggregate supply curve, so that eliminates A, B, and E. Growth of the economy will happen when the money supply increases, as demonstrated in graph D.
26. A
Stagflation is when the price level is increasing while the unemployment rate increases and slow output growth. Moving the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left will demonstrate this by increasing the price level and lowering output.
27. B
The money supply of Country X will go down because of higher interest rates. This will make their currency worth more, and since it has increased in value, Country Y can't afford as many exports from that country, so exports will decrease.
28. D
When they sell bonds on the market, they will decrease the money supply, since people are giving them money for bonds. When they sell bonds, they also increase the discount rate, which will cause an increase in interest rates.
29. B
C, D, and E are just stupid. I never even heard of A happening.
30. E
The long-run Phillips curve is a vertical line that represents the natural rate of unemployment. A and B only apply to the short-run curve. The idea is that even if the natural rate of unemployment changes, it will always revert back to normal in time, meaning it will not be affected by monetary and fiscal policy changes that affect aggregate demand. Really, I'm not making this stuff up.
31. C
Page 200 in the book has changes of input prices, changes in productivity, and changes in government regulations listed as determinants. Government spending is a determinant of aggregate demand, NOT aggregate supply. The price level is changed based the direction that the aggregate supply curve shifts, so the only possible choice is cost of input prices.
32. B
 The multiplier is equal to 5, which would make B true.
33. D
Country A sucks at making both, Country B is better overall.
34. E
A is wrong, welfare and transfer payments from the government are not included. GDP does not include any used or secondhand goods, so B is out. Nobody was paid in C. GDP is a measure of how much value was added to the economy during a year. That would mean only additions to inventories are counted, because if something was in inventory for two years, then it would have been counted twice, which would be multiple counting.
35. C
10 - 4 = 6. Nominal interest is 10%, the rate of inflation is 4%, so that means the rate of interest adjusted for inflation is only 6%.
36. C
The idea here is that the economy will self-correct, and real output will not change even with monetary policy.
37. C
There was an increase in aggregate demand caused by government spending.
The multiplier is equal to 5, which would make B true.
33. D
Country A sucks at making both, Country B is better overall.
34. E
A is wrong, welfare and transfer payments from the government are not included. GDP does not include any used or secondhand goods, so B is out. Nobody was paid in C. GDP is a measure of how much value was added to the economy during a year. That would mean only additions to inventories are counted, because if something was in inventory for two years, then it would have been counted twice, which would be multiple counting.
35. C
10 - 4 = 6. Nominal interest is 10%, the rate of inflation is 4%, so that means the rate of interest adjusted for inflation is only 6%.
36. C
The idea here is that the economy will self-correct, and real output will not change even with monetary policy.
37. C
There was an increase in aggregate demand caused by government spending.
 Output has increased, price level stayed the same.
38. A
When the price level increases, people have to buy less of a certain good. Therefore, their purchasing power has decreased.
39. C
The bank only has to keep $12,000 in reserves, since the rate is 12% and they have $100,000 in deposits. They've already loaned out $15,000 so now they only have a total of $85,000 to deal left. $70,000 of it is included as securites, which they cannot sell, so now they only have $15,000 to deal with. They have to keep at least $12,000 in reserve, so now they only have $3,000 left to loan out.
40. C
Keynesian economists believe that aggregate supply is a horizontal curve, so it will not increase or decrease, eliminating A and B. If spending is increased by $20,000 and taxes are increased by $20,000 then they've effectively canceled each other out causing no change.
41. E
If businesses believe that the economy will deteriorate in the future, then the demand for loans will decrease. The loanable funds market will only determine the long-run real interest rate, so the real interest rate will not change during the short run. The nominal interest rate will change during the short-run.
42. B
Current account is the amount of money spent on imports vs. the amount of money sold through exports. The United States has an account deficit because we give all of our money to the Chinese and they don't buy anything back from us. In other words, we spend more on imports than we make on exports. C is the exact opposite of what we want, we need to stop buying foreign goods, not buy more. D has nothing to do with international trade because it will only make a change to domestic interest rates. The capital account almost the exact opposite of the current account, and there will be a surplus. Check page 712-714 if you really don't believe me.
43. C
Increasing the real interest rate will only make the money supply go down. Everything else will increase the money supply and the economy.
44. B
Deficit-reduction means the government would increase taxes and lower spending. If the federal reserve wanted to get the opposite effect, they would lower the reserve ratio. B matches the closest.
45. D
Capital stock would decrease because interest rates have risen, so companies will spend less. The value of the dollar will rise, because now that the interest rates have rose, the money supply will go down. When the money supply goes down, it's value per dollar increases.
46. B
Never heard of the prime rate. Higher taxes will lower the price level. Decreasing oil prices would decrease the price level. If exports increase, that will raise the GDP, and raise the price level because the demand for the good is higher.
47. C
Transfer payments are for poor people on welfare. They didn't really do anything to get the money, so they never made any new goods to help the economy.
48. E
To figure out CPI, you find the basket cost of one year compared to another. You do the following math. 1993 is the base year.
5 x 6.00 + 2 x 7.00 + 3 x 12.00 = $80
5 x 5.00 + 2 x 9.00 + 3 x 19.00 = $100
1993 CPI - $80 / $80 x 100 = 100
1994 CPI - $100 / $80 x 100 = 125
125 - 100 = +25% increase
49. D
An increase in government spending will cause a rise in aggregate demand.
Output has increased, price level stayed the same.
38. A
When the price level increases, people have to buy less of a certain good. Therefore, their purchasing power has decreased.
39. C
The bank only has to keep $12,000 in reserves, since the rate is 12% and they have $100,000 in deposits. They've already loaned out $15,000 so now they only have a total of $85,000 to deal left. $70,000 of it is included as securites, which they cannot sell, so now they only have $15,000 to deal with. They have to keep at least $12,000 in reserve, so now they only have $3,000 left to loan out.
40. C
Keynesian economists believe that aggregate supply is a horizontal curve, so it will not increase or decrease, eliminating A and B. If spending is increased by $20,000 and taxes are increased by $20,000 then they've effectively canceled each other out causing no change.
41. E
If businesses believe that the economy will deteriorate in the future, then the demand for loans will decrease. The loanable funds market will only determine the long-run real interest rate, so the real interest rate will not change during the short run. The nominal interest rate will change during the short-run.
42. B
Current account is the amount of money spent on imports vs. the amount of money sold through exports. The United States has an account deficit because we give all of our money to the Chinese and they don't buy anything back from us. In other words, we spend more on imports than we make on exports. C is the exact opposite of what we want, we need to stop buying foreign goods, not buy more. D has nothing to do with international trade because it will only make a change to domestic interest rates. The capital account almost the exact opposite of the current account, and there will be a surplus. Check page 712-714 if you really don't believe me.
43. C
Increasing the real interest rate will only make the money supply go down. Everything else will increase the money supply and the economy.
44. B
Deficit-reduction means the government would increase taxes and lower spending. If the federal reserve wanted to get the opposite effect, they would lower the reserve ratio. B matches the closest.
45. D
Capital stock would decrease because interest rates have risen, so companies will spend less. The value of the dollar will rise, because now that the interest rates have rose, the money supply will go down. When the money supply goes down, it's value per dollar increases.
46. B
Never heard of the prime rate. Higher taxes will lower the price level. Decreasing oil prices would decrease the price level. If exports increase, that will raise the GDP, and raise the price level because the demand for the good is higher.
47. C
Transfer payments are for poor people on welfare. They didn't really do anything to get the money, so they never made any new goods to help the economy.
48. E
To figure out CPI, you find the basket cost of one year compared to another. You do the following math. 1993 is the base year.
5 x 6.00 + 2 x 7.00 + 3 x 12.00 = $80
5 x 5.00 + 2 x 9.00 + 3 x 19.00 = $100
1993 CPI - $80 / $80 x 100 = 100
1994 CPI - $100 / $80 x 100 = 125
125 - 100 = +25% increase
49. D
An increase in government spending will cause a rise in aggregate demand.
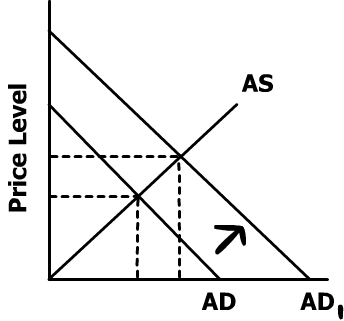 Price level and output both go up. Since the government is spending more money, the deficit also increases. Since there is more money in the economy now, interest rates will rise.
50. C
An increase in the vertical long-run aggregate supply will allow more production to take place.
51. E
If the international value of currency is higher, that means the money has more purchasing power and would lead to less inflation. Everything else will cause more inflation.
52. D
If aggregate demand suddenly decreases, natural unemployment rate would rise. There would be an increase in unplanned inventories because businesses planned to sell 80 cars, but were only able to sell 70 because the demand suddenly went down.
53. D
The bank assumed inflation would be 10% so they charged 15% interest on all their loans to make a 5% profit. Some guy went out and got a loan at 15% interest because he figured with inflation at 10% he would really only be paying 5%. However, the guy was wrong, and inflation really only increased by 5% meaning he now really has to pay 10% interest instead of the 5% like he had planned. He borrowed money at the nominal interest rate, hoping that the that inflation would rise to make it easier to pay for his loan, but instead of he was wrong and now has to pay more.
54. D
The Federal Reserve cannot change tax rates or increase government spending. If they want to reduce inflation, they would use monetary policy to reduce the money supply. In order to do that, they raise the interest rates so less people borrow money, which lowers the money supply and stops inflation.
55. B
Decreasing the money supply and increasing income taxes will only lower investment, so C is wrong. A, D, and E are not correct because the crowding out effect says that whenever the government increases spending or lowers taxes, private investments will always go down because the interest rate will rise.
56. B
The bank has one million in reserves, and has a reserve rate of around 20% since they keep excess reserves. That means they can loan out a little bit less than five million dollars. If they loan out the all the money, they will be increasing the money supply by a small amount less than five million.
57. B
A ceiling is the maximum amount someone can charge for a product. In this case, there was a ceiling put on interest rates which will make the rate lower. Since the rate is lower, more people will want loans at low interest rates so the demand increases. Since there is a limit on how high the interest rate can be, the market cannot make a lot of money, so they will reduce the amount of money they loan out, decreasing the quantity demanded.
58. E
Quantity theory of money is in the notes right before the Phillips curve section. The formula for it is MV = PQ. This is basically a fancy way of explaining inflation. If the money supply increases by 10% then there will be a 10% increase in the price level aka 10% inflation. Since the money supply has increased, the price level increased.
59. B
A raise in interest rates would decrease the United States money supply, making its value increase.
60. B
Since more money is available in Country X now to spend, the value of their money goes down. Since the value of their money has gone down, other countries can buy more of their goods at a cheaper cost, increasing their exports.
Price level and output both go up. Since the government is spending more money, the deficit also increases. Since there is more money in the economy now, interest rates will rise.
50. C
An increase in the vertical long-run aggregate supply will allow more production to take place.
51. E
If the international value of currency is higher, that means the money has more purchasing power and would lead to less inflation. Everything else will cause more inflation.
52. D
If aggregate demand suddenly decreases, natural unemployment rate would rise. There would be an increase in unplanned inventories because businesses planned to sell 80 cars, but were only able to sell 70 because the demand suddenly went down.
53. D
The bank assumed inflation would be 10% so they charged 15% interest on all their loans to make a 5% profit. Some guy went out and got a loan at 15% interest because he figured with inflation at 10% he would really only be paying 5%. However, the guy was wrong, and inflation really only increased by 5% meaning he now really has to pay 10% interest instead of the 5% like he had planned. He borrowed money at the nominal interest rate, hoping that the that inflation would rise to make it easier to pay for his loan, but instead of he was wrong and now has to pay more.
54. D
The Federal Reserve cannot change tax rates or increase government spending. If they want to reduce inflation, they would use monetary policy to reduce the money supply. In order to do that, they raise the interest rates so less people borrow money, which lowers the money supply and stops inflation.
55. B
Decreasing the money supply and increasing income taxes will only lower investment, so C is wrong. A, D, and E are not correct because the crowding out effect says that whenever the government increases spending or lowers taxes, private investments will always go down because the interest rate will rise.
56. B
The bank has one million in reserves, and has a reserve rate of around 20% since they keep excess reserves. That means they can loan out a little bit less than five million dollars. If they loan out the all the money, they will be increasing the money supply by a small amount less than five million.
57. B
A ceiling is the maximum amount someone can charge for a product. In this case, there was a ceiling put on interest rates which will make the rate lower. Since the rate is lower, more people will want loans at low interest rates so the demand increases. Since there is a limit on how high the interest rate can be, the market cannot make a lot of money, so they will reduce the amount of money they loan out, decreasing the quantity demanded.
58. E
Quantity theory of money is in the notes right before the Phillips curve section. The formula for it is MV = PQ. This is basically a fancy way of explaining inflation. If the money supply increases by 10% then there will be a 10% increase in the price level aka 10% inflation. Since the money supply has increased, the price level increased.
59. B
A raise in interest rates would decrease the United States money supply, making its value increase.
60. B
Since more money is available in Country X now to spend, the value of their money goes down. Since the value of their money has gone down, other countries can buy more of their goods at a cheaper cost, increasing their exports.
 Price level goes down, and output increases.
15. D
A is wrong. There's no such thing as world inflation. If workers suffer, businesses will always end up suffering. For E, notice the words "free international trade" which means that we wouldn't tax anything. We do tax things from other countries, and that reason is so people are encouraged buy American goods, since foreign goods won't be the cheapest anymore aka protecting United States industries.
16. D
85 - 70 = 15
17. C
It's right in the middle, and it looks like it would be the best combination for producing the maximum amount of belts and coats together.
18. A
The labor force is the amount of people who are either looking or have a job. The unemployment rate measures the percentage of people who are are either looking or have a job. Therefore, the unemployment rate measures the amount of people in the labor force who do not have jobs.
19. C
This was in the book. The classical economists all believed in laissez faire, which means the market would be self-correcting and manage itself.
20. E
C+I+G+X. What's missing?
21. B
An increase in MPC means that people are spending more. That eliminates A and C. The more people spend per consumer, the higher the multiplier. The multiplier is
Price level goes down, and output increases.
15. D
A is wrong. There's no such thing as world inflation. If workers suffer, businesses will always end up suffering. For E, notice the words "free international trade" which means that we wouldn't tax anything. We do tax things from other countries, and that reason is so people are encouraged buy American goods, since foreign goods won't be the cheapest anymore aka protecting United States industries.
16. D
85 - 70 = 15
17. C
It's right in the middle, and it looks like it would be the best combination for producing the maximum amount of belts and coats together.
18. A
The labor force is the amount of people who are either looking or have a job. The unemployment rate measures the percentage of people who are are either looking or have a job. Therefore, the unemployment rate measures the amount of people in the labor force who do not have jobs.
19. C
This was in the book. The classical economists all believed in laissez faire, which means the market would be self-correcting and manage itself.
20. E
C+I+G+X. What's missing?
21. B
An increase in MPC means that people are spending more. That eliminates A and C. The more people spend per consumer, the higher the multiplier. The multiplier is
 So let's say that the MPC is .3
So let's say that the MPC is .3
 The multiplier is 1.42. Now let's increase the MPC to .6
The multiplier is 1.42. Now let's increase the MPC to .6
 Since the MPC increased, the multiplier has increased too.
22. B
Mexicans just gave us all their worthless Pesos, so the supply of those increased. Since we got a whole bunch of them now, their value goes down.
23. D or A
Well, the answer is not $1,000 so E is out. $10,000 is not right either, because they have to store $1000 in the reserves, they just can't lend out all of it. $90,333 looks stupid. If a customer deposits $10,000 it would make complete sense that the bank can loan out $9000 now. It's a tossup between whether you want to use some crazy multiplier or not, so the answer can be either $100,000 or $9,000 depending on how smart you are.
24. D
Increases in government spending will raise the income level of consumers. It will also raise the price level, as shown here.
Since the MPC increased, the multiplier has increased too.
22. B
Mexicans just gave us all their worthless Pesos, so the supply of those increased. Since we got a whole bunch of them now, their value goes down.
23. D or A
Well, the answer is not $1,000 so E is out. $10,000 is not right either, because they have to store $1000 in the reserves, they just can't lend out all of it. $90,333 looks stupid. If a customer deposits $10,000 it would make complete sense that the bank can loan out $9000 now. It's a tossup between whether you want to use some crazy multiplier or not, so the answer can be either $100,000 or $9,000 depending on how smart you are.
24. D
Increases in government spending will raise the income level of consumers. It will also raise the price level, as shown here.
 Increases in government spending will make the money supply larger and will not affect bond prices. This will cause inflation. To combat inflation, interest rates will be increased.
25. D
Long-run economic growth always has a vertical aggregate supply curve, so that eliminates A, B, and E. Growth of the economy will happen when the money supply increases, as demonstrated in graph D.
26. A
Stagflation is when the price level is increasing while the unemployment rate increases and slow output growth. Moving the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left will demonstrate this by increasing the price level and lowering output.
27. B
The money supply of Country X will go down because of higher interest rates. This will make their currency worth more, and since it has increased in value, Country Y can't afford as many exports from that country, so exports will decrease.
28. D
When they sell bonds on the market, they will decrease the money supply, since people are giving them money for bonds. When they sell bonds, they also increase the discount rate, which will cause an increase in interest rates.
29. B
C, D, and E are just stupid. I never even heard of A happening.
30. E
The long-run Phillips curve is a vertical line that represents the natural rate of unemployment. A and B only apply to the short-run curve. The idea is that even if the natural rate of unemployment changes, it will always revert back to normal in time, meaning it will not be affected by monetary and fiscal policy changes that affect aggregate demand. Really, I'm not making this stuff up.
31. C
Page 200 in the book has changes of input prices, changes in productivity, and changes in government regulations listed as determinants. Government spending is a determinant of aggregate demand, NOT aggregate supply. The price level is changed based the direction that the aggregate supply curve shifts, so the only possible choice is cost of input prices.
32. B
Increases in government spending will make the money supply larger and will not affect bond prices. This will cause inflation. To combat inflation, interest rates will be increased.
25. D
Long-run economic growth always has a vertical aggregate supply curve, so that eliminates A, B, and E. Growth of the economy will happen when the money supply increases, as demonstrated in graph D.
26. A
Stagflation is when the price level is increasing while the unemployment rate increases and slow output growth. Moving the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left will demonstrate this by increasing the price level and lowering output.
27. B
The money supply of Country X will go down because of higher interest rates. This will make their currency worth more, and since it has increased in value, Country Y can't afford as many exports from that country, so exports will decrease.
28. D
When they sell bonds on the market, they will decrease the money supply, since people are giving them money for bonds. When they sell bonds, they also increase the discount rate, which will cause an increase in interest rates.
29. B
C, D, and E are just stupid. I never even heard of A happening.
30. E
The long-run Phillips curve is a vertical line that represents the natural rate of unemployment. A and B only apply to the short-run curve. The idea is that even if the natural rate of unemployment changes, it will always revert back to normal in time, meaning it will not be affected by monetary and fiscal policy changes that affect aggregate demand. Really, I'm not making this stuff up.
31. C
Page 200 in the book has changes of input prices, changes in productivity, and changes in government regulations listed as determinants. Government spending is a determinant of aggregate demand, NOT aggregate supply. The price level is changed based the direction that the aggregate supply curve shifts, so the only possible choice is cost of input prices.
32. B
 The multiplier is equal to 5, which would make B true.
33. D
Country A sucks at making both, Country B is better overall.
34. E
A is wrong, welfare and transfer payments from the government are not included. GDP does not include any used or secondhand goods, so B is out. Nobody was paid in C. GDP is a measure of how much value was added to the economy during a year. That would mean only additions to inventories are counted, because if something was in inventory for two years, then it would have been counted twice, which would be multiple counting.
35. C
10 - 4 = 6. Nominal interest is 10%, the rate of inflation is 4%, so that means the rate of interest adjusted for inflation is only 6%.
36. C
The idea here is that the economy will self-correct, and real output will not change even with monetary policy.
37. C
There was an increase in aggregate demand caused by government spending.
The multiplier is equal to 5, which would make B true.
33. D
Country A sucks at making both, Country B is better overall.
34. E
A is wrong, welfare and transfer payments from the government are not included. GDP does not include any used or secondhand goods, so B is out. Nobody was paid in C. GDP is a measure of how much value was added to the economy during a year. That would mean only additions to inventories are counted, because if something was in inventory for two years, then it would have been counted twice, which would be multiple counting.
35. C
10 - 4 = 6. Nominal interest is 10%, the rate of inflation is 4%, so that means the rate of interest adjusted for inflation is only 6%.
36. C
The idea here is that the economy will self-correct, and real output will not change even with monetary policy.
37. C
There was an increase in aggregate demand caused by government spending.
 Output has increased, price level stayed the same.
38. A
When the price level increases, people have to buy less of a certain good. Therefore, their purchasing power has decreased.
39. C
The bank only has to keep $12,000 in reserves, since the rate is 12% and they have $100,000 in deposits. They've already loaned out $15,000 so now they only have a total of $85,000 to deal left. $70,000 of it is included as securites, which they cannot sell, so now they only have $15,000 to deal with. They have to keep at least $12,000 in reserve, so now they only have $3,000 left to loan out.
40. C
Keynesian economists believe that aggregate supply is a horizontal curve, so it will not increase or decrease, eliminating A and B. If spending is increased by $20,000 and taxes are increased by $20,000 then they've effectively canceled each other out causing no change.
41. E
If businesses believe that the economy will deteriorate in the future, then the demand for loans will decrease. The loanable funds market will only determine the long-run real interest rate, so the real interest rate will not change during the short run. The nominal interest rate will change during the short-run.
42. B
Current account is the amount of money spent on imports vs. the amount of money sold through exports. The United States has an account deficit because we give all of our money to the Chinese and they don't buy anything back from us. In other words, we spend more on imports than we make on exports. C is the exact opposite of what we want, we need to stop buying foreign goods, not buy more. D has nothing to do with international trade because it will only make a change to domestic interest rates. The capital account almost the exact opposite of the current account, and there will be a surplus. Check page 712-714 if you really don't believe me.
43. C
Increasing the real interest rate will only make the money supply go down. Everything else will increase the money supply and the economy.
44. B
Deficit-reduction means the government would increase taxes and lower spending. If the federal reserve wanted to get the opposite effect, they would lower the reserve ratio. B matches the closest.
45. D
Capital stock would decrease because interest rates have risen, so companies will spend less. The value of the dollar will rise, because now that the interest rates have rose, the money supply will go down. When the money supply goes down, it's value per dollar increases.
46. B
Never heard of the prime rate. Higher taxes will lower the price level. Decreasing oil prices would decrease the price level. If exports increase, that will raise the GDP, and raise the price level because the demand for the good is higher.
47. C
Transfer payments are for poor people on welfare. They didn't really do anything to get the money, so they never made any new goods to help the economy.
48. E
To figure out CPI, you find the basket cost of one year compared to another. You do the following math. 1993 is the base year.
5 x 6.00 + 2 x 7.00 + 3 x 12.00 = $80
5 x 5.00 + 2 x 9.00 + 3 x 19.00 = $100
1993 CPI - $80 / $80 x 100 = 100
1994 CPI - $100 / $80 x 100 = 125
125 - 100 = +25% increase
49. D
An increase in government spending will cause a rise in aggregate demand.
Output has increased, price level stayed the same.
38. A
When the price level increases, people have to buy less of a certain good. Therefore, their purchasing power has decreased.
39. C
The bank only has to keep $12,000 in reserves, since the rate is 12% and they have $100,000 in deposits. They've already loaned out $15,000 so now they only have a total of $85,000 to deal left. $70,000 of it is included as securites, which they cannot sell, so now they only have $15,000 to deal with. They have to keep at least $12,000 in reserve, so now they only have $3,000 left to loan out.
40. C
Keynesian economists believe that aggregate supply is a horizontal curve, so it will not increase or decrease, eliminating A and B. If spending is increased by $20,000 and taxes are increased by $20,000 then they've effectively canceled each other out causing no change.
41. E
If businesses believe that the economy will deteriorate in the future, then the demand for loans will decrease. The loanable funds market will only determine the long-run real interest rate, so the real interest rate will not change during the short run. The nominal interest rate will change during the short-run.
42. B
Current account is the amount of money spent on imports vs. the amount of money sold through exports. The United States has an account deficit because we give all of our money to the Chinese and they don't buy anything back from us. In other words, we spend more on imports than we make on exports. C is the exact opposite of what we want, we need to stop buying foreign goods, not buy more. D has nothing to do with international trade because it will only make a change to domestic interest rates. The capital account almost the exact opposite of the current account, and there will be a surplus. Check page 712-714 if you really don't believe me.
43. C
Increasing the real interest rate will only make the money supply go down. Everything else will increase the money supply and the economy.
44. B
Deficit-reduction means the government would increase taxes and lower spending. If the federal reserve wanted to get the opposite effect, they would lower the reserve ratio. B matches the closest.
45. D
Capital stock would decrease because interest rates have risen, so companies will spend less. The value of the dollar will rise, because now that the interest rates have rose, the money supply will go down. When the money supply goes down, it's value per dollar increases.
46. B
Never heard of the prime rate. Higher taxes will lower the price level. Decreasing oil prices would decrease the price level. If exports increase, that will raise the GDP, and raise the price level because the demand for the good is higher.
47. C
Transfer payments are for poor people on welfare. They didn't really do anything to get the money, so they never made any new goods to help the economy.
48. E
To figure out CPI, you find the basket cost of one year compared to another. You do the following math. 1993 is the base year.
5 x 6.00 + 2 x 7.00 + 3 x 12.00 = $80
5 x 5.00 + 2 x 9.00 + 3 x 19.00 = $100
1993 CPI - $80 / $80 x 100 = 100
1994 CPI - $100 / $80 x 100 = 125
125 - 100 = +25% increase
49. D
An increase in government spending will cause a rise in aggregate demand.
 Price level and output both go up. Since the government is spending more money, the deficit also increases. Since there is more money in the economy now, interest rates will rise.
50. C
An increase in the vertical long-run aggregate supply will allow more production to take place.
51. E
If the international value of currency is higher, that means the money has more purchasing power and would lead to less inflation. Everything else will cause more inflation.
52. D
If aggregate demand suddenly decreases, natural unemployment rate would rise. There would be an increase in unplanned inventories because businesses planned to sell 80 cars, but were only able to sell 70 because the demand suddenly went down.
53. D
The bank assumed inflation would be 10% so they charged 15% interest on all their loans to make a 5% profit. Some guy went out and got a loan at 15% interest because he figured with inflation at 10% he would really only be paying 5%. However, the guy was wrong, and inflation really only increased by 5% meaning he now really has to pay 10% interest instead of the 5% like he had planned. He borrowed money at the nominal interest rate, hoping that the that inflation would rise to make it easier to pay for his loan, but instead of he was wrong and now has to pay more.
54. D
The Federal Reserve cannot change tax rates or increase government spending. If they want to reduce inflation, they would use monetary policy to reduce the money supply. In order to do that, they raise the interest rates so less people borrow money, which lowers the money supply and stops inflation.
55. B
Decreasing the money supply and increasing income taxes will only lower investment, so C is wrong. A, D, and E are not correct because the crowding out effect says that whenever the government increases spending or lowers taxes, private investments will always go down because the interest rate will rise.
56. B
The bank has one million in reserves, and has a reserve rate of around 20% since they keep excess reserves. That means they can loan out a little bit less than five million dollars. If they loan out the all the money, they will be increasing the money supply by a small amount less than five million.
57. B
A ceiling is the maximum amount someone can charge for a product. In this case, there was a ceiling put on interest rates which will make the rate lower. Since the rate is lower, more people will want loans at low interest rates so the demand increases. Since there is a limit on how high the interest rate can be, the market cannot make a lot of money, so they will reduce the amount of money they loan out, decreasing the quantity demanded.
58. E
Quantity theory of money is in the notes right before the Phillips curve section. The formula for it is MV = PQ. This is basically a fancy way of explaining inflation. If the money supply increases by 10% then there will be a 10% increase in the price level aka 10% inflation. Since the money supply has increased, the price level increased.
59. B
A raise in interest rates would decrease the United States money supply, making its value increase.
60. B
Since more money is available in Country X now to spend, the value of their money goes down. Since the value of their money has gone down, other countries can buy more of their goods at a cheaper cost, increasing their exports.
Price level and output both go up. Since the government is spending more money, the deficit also increases. Since there is more money in the economy now, interest rates will rise.
50. C
An increase in the vertical long-run aggregate supply will allow more production to take place.
51. E
If the international value of currency is higher, that means the money has more purchasing power and would lead to less inflation. Everything else will cause more inflation.
52. D
If aggregate demand suddenly decreases, natural unemployment rate would rise. There would be an increase in unplanned inventories because businesses planned to sell 80 cars, but were only able to sell 70 because the demand suddenly went down.
53. D
The bank assumed inflation would be 10% so they charged 15% interest on all their loans to make a 5% profit. Some guy went out and got a loan at 15% interest because he figured with inflation at 10% he would really only be paying 5%. However, the guy was wrong, and inflation really only increased by 5% meaning he now really has to pay 10% interest instead of the 5% like he had planned. He borrowed money at the nominal interest rate, hoping that the that inflation would rise to make it easier to pay for his loan, but instead of he was wrong and now has to pay more.
54. D
The Federal Reserve cannot change tax rates or increase government spending. If they want to reduce inflation, they would use monetary policy to reduce the money supply. In order to do that, they raise the interest rates so less people borrow money, which lowers the money supply and stops inflation.
55. B
Decreasing the money supply and increasing income taxes will only lower investment, so C is wrong. A, D, and E are not correct because the crowding out effect says that whenever the government increases spending or lowers taxes, private investments will always go down because the interest rate will rise.
56. B
The bank has one million in reserves, and has a reserve rate of around 20% since they keep excess reserves. That means they can loan out a little bit less than five million dollars. If they loan out the all the money, they will be increasing the money supply by a small amount less than five million.
57. B
A ceiling is the maximum amount someone can charge for a product. In this case, there was a ceiling put on interest rates which will make the rate lower. Since the rate is lower, more people will want loans at low interest rates so the demand increases. Since there is a limit on how high the interest rate can be, the market cannot make a lot of money, so they will reduce the amount of money they loan out, decreasing the quantity demanded.
58. E
Quantity theory of money is in the notes right before the Phillips curve section. The formula for it is MV = PQ. This is basically a fancy way of explaining inflation. If the money supply increases by 10% then there will be a 10% increase in the price level aka 10% inflation. Since the money supply has increased, the price level increased.
59. B
A raise in interest rates would decrease the United States money supply, making its value increase.
60. B
Since more money is available in Country X now to spend, the value of their money goes down. Since the value of their money has gone down, other countries can buy more of their goods at a cheaper cost, increasing their exports.